

It increases cardiac output (CO) by increased cardiac contractility, leading to increased coronary artery blood flow. The extent of the steal of systemic circulation by AVF is not known under such conditions.ĭobutamine is a positive inotropic agent directly stimulating the β 1 adrenergic receptors. However, patients with AVFs of any origin can be exposed to different critical conditions requiring inotropic or vasopressor support, or states with sudden increase or decrease in cardiac output (e.g., sepsis, acute heart failure, etc.). Our working group has already created an animal model of hyperkinetic circulation with the use of a high flow AVF. The detrimental effect of the AVF on brain perfusion and tissue oxygenation, or on transplanted kidney perfusion has been described previously in humans ( Laranjinha et al., 2019 Kovarova et al., 2021). The term effective cardiac output represents the difference of total cardiac output and AVF flow ( Basile et al., 2007). These experiments highlight the detrimental role of a large AVF in these critical conditions’ models.Ī large arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is a low-resistant circuit that can substantially affect the hemodynamics and organ perfusion since a significant part of the cardiac output (10%–40% in humans) is shunted from systemic arteries to veins.
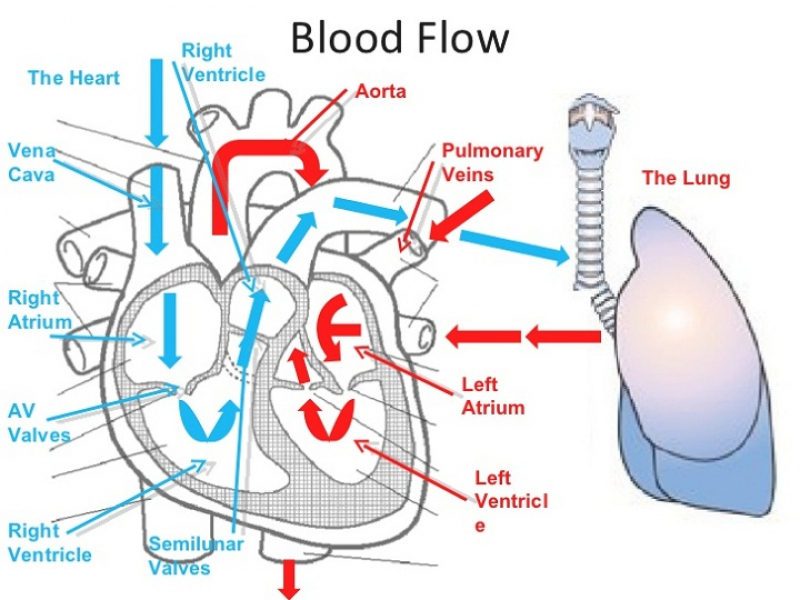
The ratio of shunt flow to cardiac output depended on systemic vascular resistance. Therefore, the effective cardiac output decreased.Ĭonclusion: In abovementioned extreme hemodynamic conditions the AVF flow was always directly proportional to systemic perfusion pressure. AVF blood flow also dropped significantly and proportionally to pressure, but Qa/CO ratio did not change. The effective cardiac output using the heart failure model leading to decrease of carotid artery flow and worsening of brain and peripheral tissue oximetry.

Carotid artery blood flow increased significantly after dobutamine infusion by approximately 30%, coronary flow velocity increased significantly only in closed AVF state. Dobutamine substantially increased cardiac output with insignificant effect on AVF flow and mean arterial pressure. Effective cardiac output increased, leading to insignificant improvement in organ perfusion. AVF flow (Qa) rise correlated with mean arterial pressure increase (+20% R = 0.97, p = 0.0001). Results: Continuous infusion of norepinephrine with opened AVF significantly increased mean arterial pressure (+20%) and total cardiac output (CO) (+36%), but vascular resistance remained virtually unchanged. Measurements were taken with opened and closed arteriovenous fistula. Three interventions were performed–moderate dose of norepinephrine (0.25 ug/kg/min), moderate dose of dobutamine (10 ug/kg/min) and rapid right ventricle pacing to simulate low cardiac output state with mean arterial pressure under 60 mmHg. Continuous hemodynamic monitoring was performed throughout the protocol. AVF was created by connecting two high-diameter ECMO cannulas inserted in the femoral artery and vein. Methods: The protocol was performed on nine domestic female pigs under general anesthesia. We used norepinephrine to create systemic vasoconstriction, dobutamine to create high cardiac output, and rapid right ventricle pacing as a model of acute heart failure in a porcine model of high-flow AVF circulation. The extent of its’ effect in critical states has not been elucidated yet. 32nd Surgical Clinic-Cardiovascular Surgery, General University Hospital in Prague and 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechiaīackground: A large arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is a low-resistant circuit that affects organ perfusion and systemic hemodynamics even in standard conditions.2Institute of Physiology, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechia.
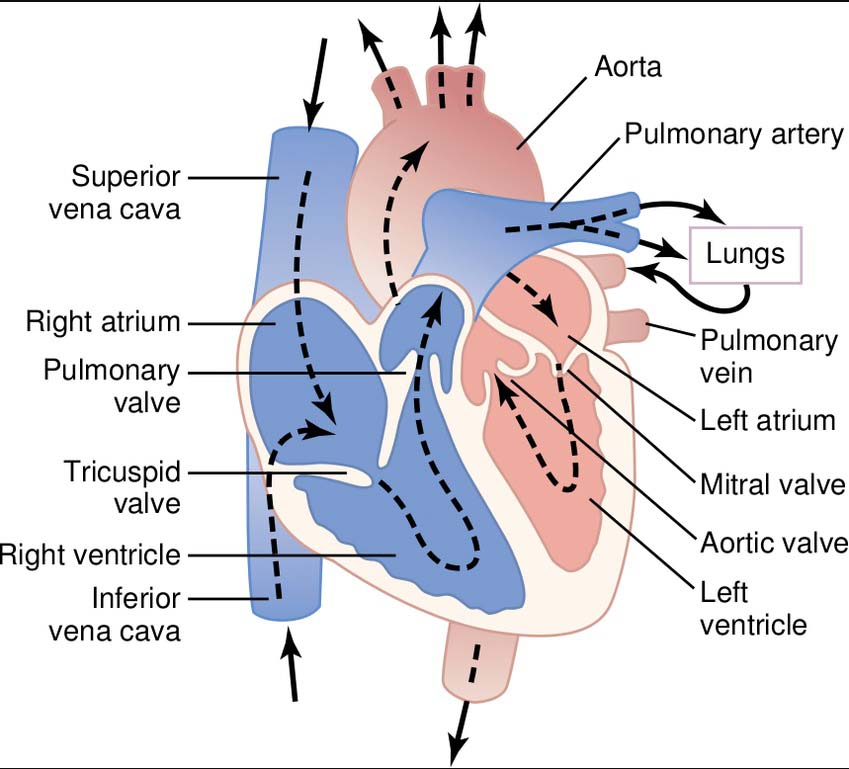
13rd Department of Internal Medicine, General University Hospital in Prague and 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
